Pronouns are words such as he, her, your, it and this used in place of nouns or noun phrases. They are of the following types.
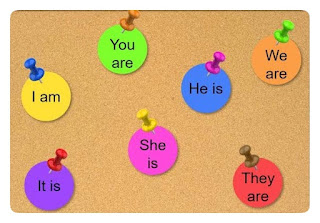
- Personal pronouns stand for the speaker (first person), the person spoken to (second person), and the person, animal, place or thing that is neither the speaker not the spoken to (third person). In English, the personal pronouns used as subjects in sentences are I, we, you, he, she, they and it. The corresponding personal pronouns used as objects are me, us, you, him, her, them and it.
- Possessive pronouns are used in place of nouns with an apostrophe and -s, such as Suma's, to indicate the meaning of belonging or possession. They are mine, ours, yours, his, her and theirs. Examples are This is not Shireen's file. The bag is not Smita's; hers is larger.
- Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and the object of a verb (or preposition) both refer to the same person, animal, place or thing, for example, myself, ourselves, yourself, yourselves, himself, herself, itself and themselves. They can also be called emphatic pronouns.
- Demonstrative pronouns are for example, this, that, these and those.
- Indefinite pronouns are also used in place of nouns when we do not know or do not want to specify the identity and number of the person or thing we are referring to, for example, some, any, others, another, someone, somebody, something, everyone, everybody, everything, anyone, anybody, anything, one, no one, nobody and nothing.
- Interrogative pronouns are who, whom, whose, which, how and what.
- Relative pronouns who, whom, whose, which and that, refer to nouns coming before them in the sentence.
- Distributive pronouns, for example, each, either, neither, each other, one another.



Comments
Post a Comment